ORE Studio Telemetry Component
Observability library providing logging and distributed tracing for ORE Studio.
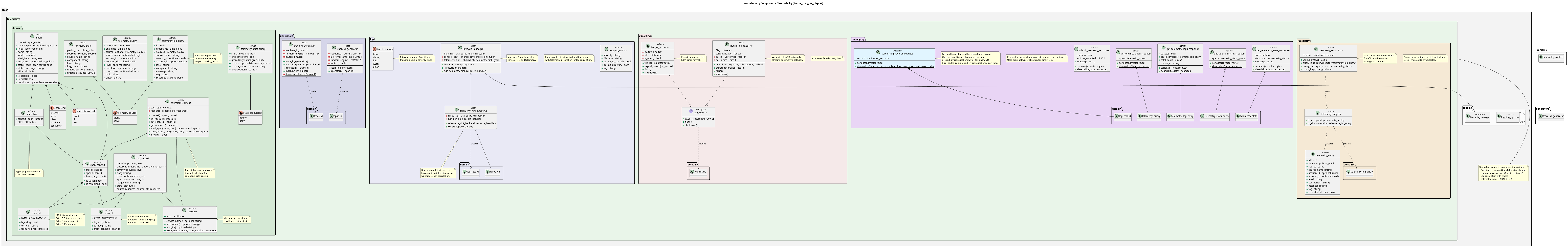
Component Architecture
Diagram:
The telemetry component provides unified observability infrastructure aligned with OpenTelemetry concepts. Key features:
- Logging: Boost.Log integration with lifecycle management
- Tracing: OpenTelemetry-aligned trace_id and span_id generation
- Correlation: Log records linked to traces and spans for distributed debugging
- Export: JSON Lines file exporter for log shipping
- Resources: Machine/service identity with automatic host_id derivation
The component is organized into the following namespaces:
| Namespace | Purpose |
|---|---|
domain |
Core types: trace_id, span_id, log_record, resource |
generators |
ID generators for traces and spans |
log |
Boost.Log integration and lifecycle management |
exporting |
Exporters for log records (file, hybrid) |
messaging |
Protocol types for server communication |
repository |
Database persistence for telemetry logs |
Logging Infrastructure
The logging infrastructure is built on Boost.Log and provides:
- Per-module loggers with channel-based filtering
- Configurable severity levels (trace, debug, info, warn, error)
- Console and file sinks with rotation
- Thread-safe asynchronous logging
Basic Usage
#include "ores.logging/make_logger.hpp" namespace { const std::string logger_name("my_component"); auto& lg() { static auto r = telemetry::log::make_channel_logger(logger_name); return r; } } void do_work() { BOOST_LOG_SEV(lg(), telemetry::log::info) << "Starting operation"; // ... work ... BOOST_LOG_SEV(lg(), telemetry::log::debug) << "Operation complete"; }
Lifecycle Management
The lifecycle_manager class handles initialization and shutdown of all logging
sinks. Applications create a single instance at startup:
#include "ores.telemetry/log/lifecycle_manager.hpp" int main() { telemetry::log::logging_options opts; opts.severity = "info"; opts.filename = "app.log"; opts.output_directory = "/var/log/ores"; opts.output_to_console = true; telemetry::log::lifecycle_manager lm(opts); // ... application runs ... // Logging is automatically shut down when lm goes out of scope }
Telemetry Export
The telemetry component can export log records to external systems for centralized log aggregation and analysis. This is an opt-in feature that requires explicit configuration.
Enabling Log Export
To enable log export, add a telemetry sink to the lifecycle manager:
#include "ores.telemetry/log/lifecycle_manager.hpp" #include "ores.telemetry/exporting/file_log_exporter.hpp" #include "ores.telemetry/domain/resource.hpp" int main() { // Create logging with standard options telemetry::log::logging_options opts; opts.severity = "info"; opts.filename = "app.log"; opts.output_directory = "/var/log/ores"; telemetry::log::lifecycle_manager lm(opts); // Create resource describing this service auto resource = telemetry::domain::resource::from_environment( "ores-service", "1.0.0"); // Create file exporter for JSON Lines output auto exporter = std::make_shared<telemetry::exporting::file_log_exporter>( "/var/log/ores/telemetry.jsonl"); // Add telemetry sink - all logs now also exported lm.add_telemetry_sink(resource, [exporter](auto rec) { exporter->export_record(std::move(rec)); }); // ... application runs ... }
Export Format
The file_log_exporter writes log records in JSON Lines format (one JSON object
per line), making it easy to ingest into log aggregation systems like Elasticsearch,
Loki, or Splunk.
Example output:
{"timestamp":"2025-01-15T10:30:45.123Z","severity":"INFO","body":"Connection established","logger":"comms.client","trace_id":"0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef","span_id":"fedcba9876543210","service":"ores-service"}
{"timestamp":"2025-01-15T10:30:45.456Z","severity":"DEBUG","body":"Received handshake response","logger":"comms.protocol"}
Fields in exported records:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
timestamp |
ISO 8601 timestamp with millisecond precision |
severity |
Log level (TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL) |
body |
The log message |
logger |
Name of the logger/component |
trace_id |
32-character hex trace ID (if present) |
span_id |
16-character hex span ID (if present) |
service |
Service name from resource |
Trace Correlation
Log records can be correlated with distributed traces by including trace_id and
span_id attributes. When logs are exported with trace context, they can be
linked to specific operations in a distributed tracing system.
How It Works
- The
telemetry_sink_backendintercepts all Boost.Log records - It extracts
trace_idandspan_idfrom log attributes (if present) - It creates a
domain::log_recordwith the trace context - The handler (exporter) writes the record with trace correlation
Adding Trace Context to Logs
To correlate logs with traces, add trace attributes when logging:
#include "ores.telemetry/domain/telemetry_context.hpp" void handle_request(const telemetry::domain::telemetry_context& ctx) { // The context carries trace_id and span_id through the call chain BOOST_LOG_SEV(lg(), telemetry::log::info) << boost::log::add_value("trace_id", ctx.get_trace_id().to_hex()) << boost::log::add_value("span_id", ctx.get_span_id().to_hex()) << "Processing request"; }
Custom Exporters
You can implement custom exporters by implementing the log_exporter interface:
#include "ores.telemetry/exporting/log_exporter.hpp" class my_exporter : public telemetry::exporting::log_exporter { public: void export_record(telemetry::domain::log_record record) override { // Send to your log aggregation system } void flush() override { // Flush any buffered records } void shutdown() override { // Clean up resources } };
Server-Side Telemetry Persistence
The telemetry system supports centralized log storage in PostgreSQL with TimescaleDB for time-series optimizations. This allows clients to stream logs to the server for centralized analysis, aggregation, and long-term retention.
Architecture
┌─────────────┐ submit_telemetry ┌──────────────────┐
│ Clients │ ──────────────────► │ ores.comms.service│
│ (qt, shell) │ │ │
│ │ ◄────────────────── │ Also logs here │
│ │ get_telemetry_* │ │ │
└─────────────┘ └────────┼──────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────┐
│ PostgreSQL │
│ telemetry_logs │
│ (hypertable) │
└────────────────────┘
Database Schema
Logs are stored in a TimescaleDB hypertable with the following structure:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
UUID | Unique log entry identifier |
timestamp |
TIMESTAMPTZ | When the log was created (partition key) |
source |
TEXT | 'client' or 'server' |
source_name |
TEXT | e.g., 'ores.qt', 'ores.comms.shell', 'ores.comms.service' |
session_id |
UUID | Client session (NULL for server logs) |
account_id |
UUID | Logged-in user (NULL if not authenticated) |
level |
TEXT | trace, debug, info, warn, error |
component |
TEXT | Logger name |
message |
TEXT | Log message body |
tag |
TEXT | Optional categorization tag |
TimescaleDB features:
- 1-day chunks for optimal query performance
- Compression after 3 days
- 30-day retention for raw logs
- Continuous aggregates for hourly/daily statistics
Protocol Messages
The telemetry subsystem uses message types in the 0x5000-0x5FFF range:
| Message Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
submit_telemetry_request |
0x5001 | Submit batch of log entries |
submit_telemetry_response |
0x5002 | Acknowledge submission |
get_telemetry_logs_request |
0x5010 | Query logs with filters |
get_telemetry_logs_response |
0x5011 | Return matching log entries |
get_telemetry_stats_request |
0x5020 | Query aggregated statistics |
get_telemetry_stats_response |
0x5021 | Return statistics entries |
Client-Side Streaming
Clients can stream their logs to the server in real-time using the
telemetry_streaming_service. This service:
- Captures all Boost.Log records via a sink backend
- Batches entries to reduce network overhead
- Sends batches on timer or when batch is full
- Gracefully handles disconnections
Qt Client Integration
The Qt client enables streaming via TelemetrySettingsDialog:
#include "ores.comms/service/telemetry_streaming_service.hpp" // In main.cpp or ClientManager: if (TelemetrySettingsDialog::isStreamingEnabled()) { comms::service::telemetry_streaming_options opts{ .source_name = "ores.qt", .source_version = ORES_VERSION, .batch_size = TelemetrySettingsDialog::streamingBatchSize(), .flush_interval = std::chrono::seconds( TelemetrySettingsDialog::streamingFlushInterval()) }; clientManager->enableStreaming(opts); }
Shell Client Integration
The shell client configures streaming via command line:
// In application.cpp: if (streaming_options_ && session.is_connected()) { streaming_service = std::make_unique< comms::service::telemetry_streaming_service>( session.get_client(), *streaming_options_); streaming_service->start(); }
Streaming Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
source_name |
- | Identifies the client (required) |
source_version |
- | Client version string |
batch_size |
100 | Max entries per batch |
flush_interval |
5s | Time between forced flushes |
Component Split: ores.logging
The core logging infrastructure was extracted into a separate ores.logging
component to break a circular dependency between ores.telemetry and
ores.database.
Motivation
The original design had:
ores.telemetryproviding logging to all components includingores.databaseores.telemetryneedingores.databasefor telemetry persistence
This created: ores.telemetry → ores.database → ores.telemetry
Solution
Extract pure logging infrastructure to ores.logging:
| Component | Responsibility |
|---|---|
ores.logging |
Core logging: severity, make_logger, lifecycle |
ores.telemetry |
Tracing, export, server persistence |
ores.database |
Depends on ores.logging (no cycle) |
ores.logging Contents
ores.logging/
├── include/ores.logging/
│ ├── severity_level.hpp # OpenTelemetry-compatible severity
│ ├── boost_severity.hpp # Boost.Log severity enum
│ ├── make_logger.hpp # Logger factory
│ ├── lifecycle_manager.hpp # Virtual base class
│ ├── logging_options.hpp # Configuration options
│ ├── logging_configuration.hpp # Boost.Log setup
│ └── logging_exception.hpp # Exception type
└── src/
├── lifecycle_manager.cpp
├── logging_options.cpp
└── logging_configuration.cpp
Backward Compatibility
The ores.telemetry/log/ headers provide forwarding to ores.logging types,
allowing existing code to continue working without changes:
// These still work: #include "ores.logging/make_logger.hpp" #include "ores.telemetry/log/lifecycle_manager.hpp" // They forward to ores.logging equivalents
Future Enhancements
Planned features for the telemetry component:
- OTLP exporter for direct integration with OpenTelemetry collectors
- Span creation and management APIs
- Metrics support
- Baggage propagation for cross-service context
- HTTP endpoints for telemetry submission and query
| Top: Documentation | Previous: System Model |