ORE Studio Platform Component
Cross-platform abstractions for operating system services in ORE Studio.
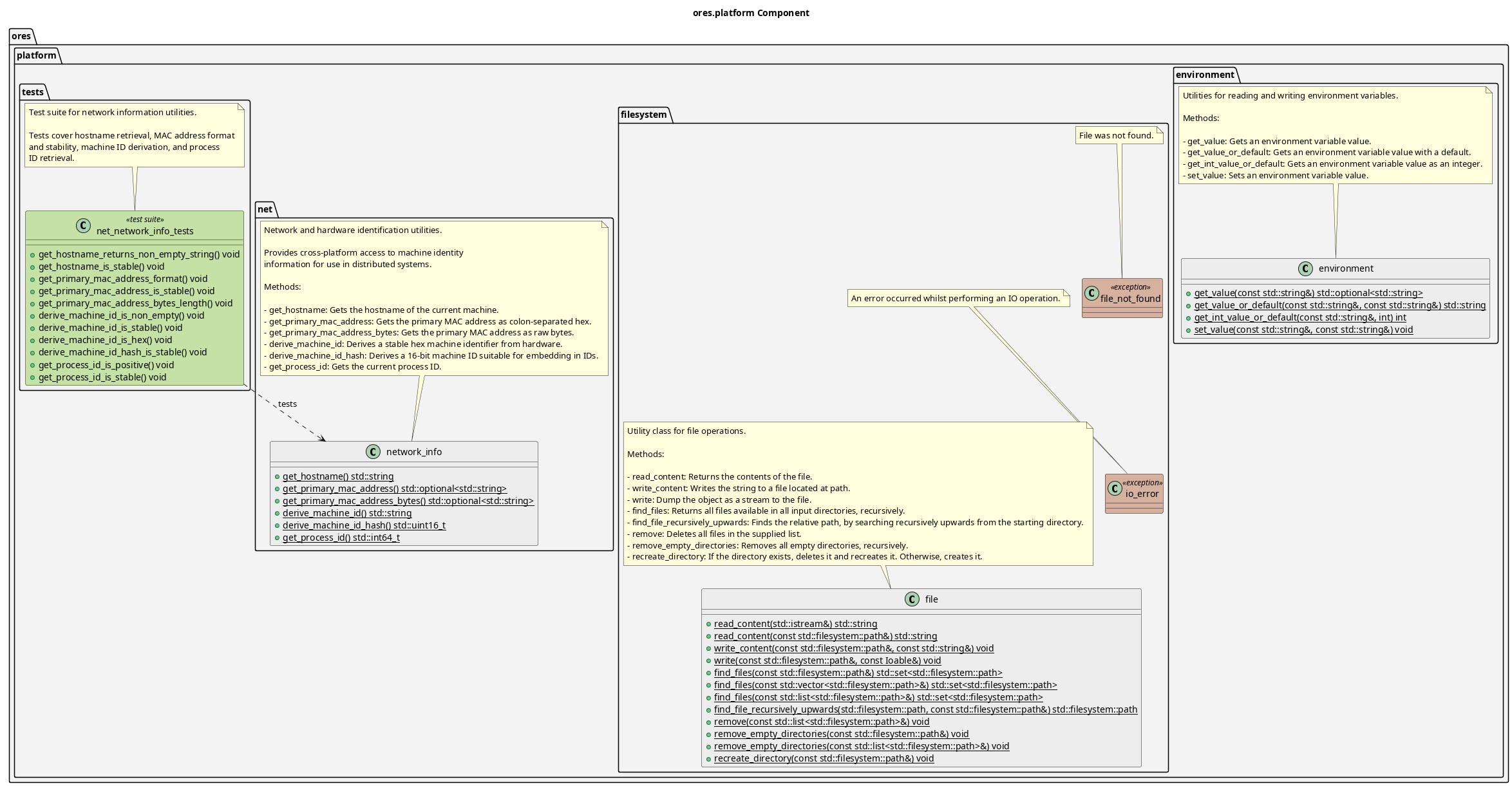
Component Architecture
Diagram:
Provides cross-platform abstractions for OS-level functionality that varies between platforms. This component isolates platform-specific code, allowing higher layers to use consistent APIs. Key namespaces:
- environment: Environment variable access with type conversion
- filesystem: File I/O utilities, directory operations, recursive search
- net: Network and hardware identification (hostname, MAC address, machine ID)
- time: Cross-platform time conversion utilities
This module depends only on ores.utility, making it part of the foundation layer upon which telemetry and other components are built.
| Namespace | Purpose |
|---|---|
environment |
Environment variable access with type conversion |
filesystem |
File operations and directory manipulation |
net |
Network info, machine identity, process ID |
time |
Cross-platform time_t to tm struct conversion |
Filesystem Utilities
The filesystem namespace provides utilities for common file operations:
- file: Core file operations class with methods for reading, writing, and finding files recursively
- file_not_found: Exception thrown when a requested file does not exist
- io_error: Exception thrown when an I/O operation fails
Basic Usage
#include "ores.platform/filesystem/file.hpp" using ores::platform::filesystem::file; // Read file contents std::string content = file::read_content("/path/to/file.txt"); // Write content to file file::write_content("/path/to/output.txt", "Hello, World!"); // Find all files in a directory recursively auto files = file::find_files("/path/to/directory"); // Find file by searching upwards from a starting directory auto config = file::find_file_recursively_upwards( std::filesystem::current_path(), "config.yml");
Environment Variables
The environment namespace provides utilities for reading and writing
environment variables with type conversion:
#include "ores.platform/environment/environment.hpp" using ores::platform::environment::environment; // Get optional value auto value = environment::get_value("MY_VAR"); if (value) { // use *value } // Get with default std::string host = environment::get_value_or_default("HOST", "localhost"); // Get as integer with default int port = environment::get_int_value_or_default("PORT", 8080); // Set a value environment::set_value("MY_VAR", "new_value");
Network Information
The net namespace provides utilities for retrieving network and hardware
identification information, useful for distributed systems:
#include "ores.platform/net/network_info.hpp" using namespace ores::platform::net; // Get hostname std::string hostname = get_hostname(); // Get primary MAC address (formatted as "00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e") auto mac = get_primary_mac_address(); // Derive stable machine identifier (hex-encoded hash) std::string machine_id = derive_machine_id(); // Get 16-bit machine ID hash for embedding in IDs std::uint16_t id_hash = derive_machine_id_hash(); // Get current process ID std::int64_t pid = get_process_id();
Time Utilities
The time namespace provides cross-platform wrappers for time conversion
functions that differ between POSIX and Windows:
#include "ores.platform/time/time_utils.hpp" using ores::platform::time::time_utils; std::time_t now = std::time(nullptr); std::tm utc_time{}; std::tm local_time{}; // Convert to UTC (cross-platform) time_utils::gmtime_safe(&now, &utc_time); // Convert to local time (cross-platform) time_utils::localtime_safe(&now, &local_time);
| Top: Documentation | Previous: System Model |